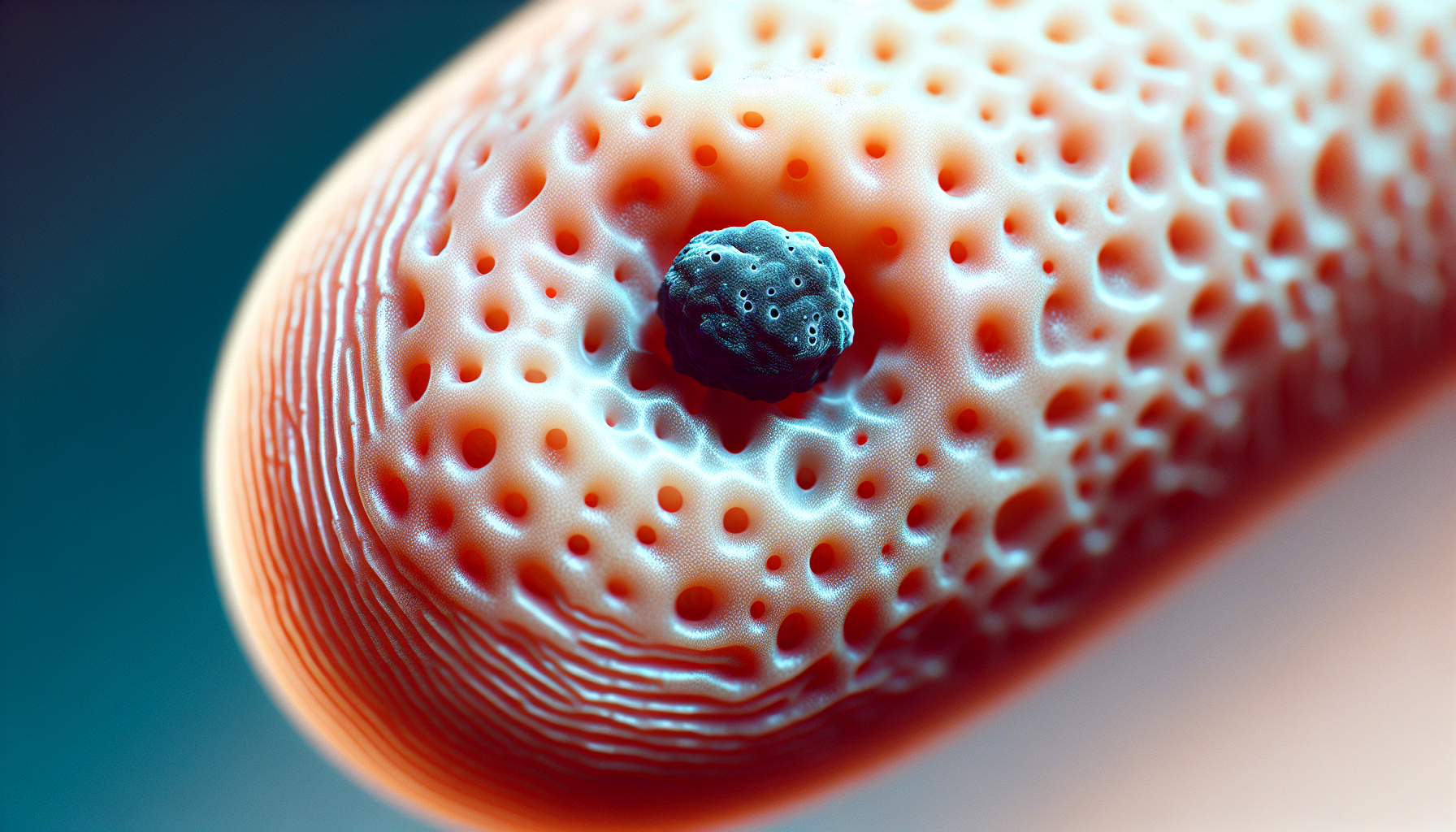
Blackheads: those stubborn, pesky little blemishes that seem to appear out of nowhere and refuse to budge. But have you ever wondered what exactly is the culprit behind their formation? It’s time to uncover the mysterious stuff that makes blackheads come out. Whether you’re someone who battles with these little nuisances regularly or simply curious about the science behind skin concerns, this article will shed light on the reasons behind blackheads and the factors that contribute to their development. Get ready to unveil the secrets hiding inside those tiny, annoying dots!
Understanding Blackheads
Definition of Blackheads
Blackheads are a common type of skin blemish characterized by small, dark-colored bumps on the skin’s surface. They are a form of acne known as open comedones and are caused by clogged hair follicles and pores. Blackheads can appear on various parts of the body, but they are most commonly found on the face, particularly the nose, chin, and forehead.
Formation of Blackheads
Blackheads form when the hair follicles and pores on the skin become clogged with oil, dead skin cells, and other debris. The clog creates a plug that prevents the natural flow of oil, known as sebum, from reaching the skin’s surface. As the sebum accumulates in the follicle, it oxidizes and turns dark, giving the blackhead its characteristic appearance.
Common Locations for Blackheads
While blackheads can appear anywhere on the body, there are certain areas where they are more commonly found. The most common locations for blackheads include:
-
Nose: The nose is particularly prone to blackheads due to the presence of a high concentration of oil glands.
-
Chin: The chin is another area where blackheads often develop, especially in individuals with oily or combination skin types.
-
Forehead: Blackheads can also appear on the forehead, especially in individuals who have a tendency to sweat heavily or wear tight-fitting headgear.
-
Cheeks: While less common than the aforementioned areas, blackheads can also be found on the cheeks, particularly in individuals with larger or more active oil glands.
The Science behind Blackheads
Role of Sebum
Sebum is an oily substance produced by the sebaceous glands, which are located within the hair follicles. It plays a crucial role in keeping the skin moisturized and acts as a protective barrier against environmental factors. However, when the production of sebum becomes excessive, it can contribute to the formation of blackheads.
Hair Follicles and Pores
Hair follicles are small cavities within the skin that contain the root of a hair. Pores, on the other hand, are the openings of the hair follicles. Both hair follicles and pores can become clogged with a combination of sebum, dead skin cells, and other debris, leading to the formation of blackheads.
Keratinization Process
The keratinization process refers to the natural shedding of dead skin cells from the skin’s surface. However, in individuals prone to blackheads, the shedding process can become disrupted, causing an accumulation of dead skin cells within the hair follicles and pores. This, in turn, increases the risk of blackhead formation.
The Role of Bacteria
While bacteria do not directly cause blackheads, they can contribute to their formation. The presence of bacteria on the skin can trigger an inflammatory response, leading to an increase in sebum production. Additionally, the bacteria can break down sebum and other substances within the clogged hair follicles, further contributing to the formation and persistence of blackheads.
Factors Contributing to Blackhead Formation
Excessive Sebum Production
Excessive sebum production is one of the primary factors contributing to blackhead formation. Individuals with oily or combination skin types are more prone to blackheads due to their increased sebum production.
Hormonal Influence
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during puberty, pregnancy, or menstruation, can lead to an increase in sebum production and, consequently, blackhead formation. Hormonal fluctuations can also affect the shedding of dead skin cells, further exacerbating the risk of blackhead development.
Genetics
Genetics can play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to blackheads. If your parents or close relatives have a history of blackheads or acne, you may be more prone to developing them as well.
Improper Skin Care
Inadequate skin care practices, such as not properly cleansing or exfoliating the skin, can contribute to blackhead formation. When the skin is not thoroughly cleansed, excess oil, dead skin cells, and other debris can accumulate, increasing the likelihood of clogged hair follicles and pores.
Environmental Factors
Certain environmental factors can also contribute to blackhead formation. Exposure to pollutants, humid weather conditions, and wearing heavy makeup or skincare products can all increase the risk of pore blockage and blackhead development.
Cosmetic Products
Using certain cosmetic products, particularly those that are comedogenic or contain pore-clogging ingredients, can contribute to blackhead formation. It is essential to choose non-comedogenic products that do not block the pores and aggravate blackhead formation.
The Content of Blackheads
Sebum
Sebum, the natural oil produced by the sebaceous glands, is a primary component of blackheads. Excess sebum production or improper sebum composition can contribute to the formation of blackheads.
Dead Skin Cells
An accumulation of dead skin cells is another vital component of blackheads. When the shedding of dead skin cells becomes disrupted, as in the case of individuals prone to blackheads, these cells can build up and mix with sebum, leading to clogged hair follicles and pore blockage.
Bacteria
Although not a direct cause of blackheads, the presence of bacteria on the skin can contribute to their formation. Bacteria can trigger inflammation and break down sebum, further exacerbating blackhead development.
Dirt and Debris
External factors such as dirt, pollution, and debris from the environment can also contribute to blackhead formation. These substances can mix with sebum and dead skin cells, forming plugs that block the hair follicles and pores.
Oxidized Melanin
Oxidized melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color, can also contribute to the dark appearance of blackheads. When sebum and dead skin cells within the hair follicles and pores oxidize, they can darken, giving blackheads their characteristic color.
Differentiating Blackheads from Other Skin Blemishes
Blackheads vs. Whiteheads
While blackheads are open comedones, whiteheads are closed comedones. Whiteheads are characterized by small, flesh-colored or white bumps on the skin’s surface. The primary difference between blackheads and whiteheads is that blackheads are exposed to air, causing the oxidation of sebum and subsequent darkening.
Blackheads vs. Pimples
Blackheads and pimples are both forms of acne, but they have distinct characteristics. Pimples, also known as papules and pustules, are inflamed lesions that can be red, swollen, and filled with pus. Unlike blackheads, pimples are not open to the surface and can be painful or tender to the touch.
Blackheads vs. Milia
Milia are small, white bumps that often appear around the eyes, cheeks, and nose. Unlike blackheads, milia are not caused by pore blockage but rather by trapped keratin, a protein found in the outer layer of the skin. Milia are typically firmer than blackheads and do not darken upon exposure to air.
Blackheads vs. Sebaceous Filaments
Sebaceous filaments are often mistaken for blackheads due to their similar appearance. However, sebaceous filaments are a normal part of the skin and serve the purpose of carrying sebum to the skin’s surface. They are typically lighter in color, less defined, and less noticeable than blackheads.
Common Misconceptions about Blackheads
Blackheads are Caused by Dirt
Contrary to popular belief, blackheads are not caused by dirt. The dark appearance is due to the oxidation of sebum within the clogged hair follicles and pores. Keeping the skin clean and practicing proper skincare can help prevent blackhead formation, but they are not solely caused by dirt.
Only People with Oily Skin Get Blackheads
While individuals with oily skin are more prone to blackheads, they can affect people with all skin types. Factors like hormonal changes, genetics, and environmental factors can contribute to blackhead formation, regardless of skin type.
Blackheads are a Sign of Poor Hygiene
Having blackheads does not necessarily indicate poor hygiene. Blackhead formation is influenced by various factors, including genetics and hormonal changes. Proper cleansing and exfoliation are important for preventing blackheads, but they are not solely caused by poor hygiene.
Squeezing Blackheads is the Best Solution
Squeezing or picking at blackheads can worsen the condition and cause inflammation, scarring, or infection. Gentle extraction techniques performed by professionals are a safer and more effective solution for removing blackheads.
Blackheads will Disappear on their Own
Blackheads may improve with proper skincare and treatment, but they typically do not disappear on their own. Without intervention, blackheads can persist and potentially worsen over time.
Removing Blackheads Permanently
While blackheads can be treated and managed, completely removing them permanently can be challenging. Consistent skincare practices and professional treatments can help reduce their appearance and prevent future blackhead formation.
Prevention and Treatment of Blackheads
Adopting a Proper Skincare Routine
Establishing a consistent skincare routine is crucial in preventing blackheads. This includes cleansing, exfoliating, and moisturizing the skin regularly to remove excess oil, dead skin cells, and other impurities.
Cleansing and Exfoliating
Regularly cleansing the skin with a gentle cleanser helps remove excess oil and impurities. Exfoliation, either physical or chemical, can aid in the removal of dead skin cells and unclog the pores, reducing the risk of blackhead formation.
Using Non-Comedogenic Products
Using non-comedogenic products that do not clog the pores can help prevent blackheads. Look for skincare and cosmetic products labeled as non-comedogenic to minimize the risk of pore blockage.
Avoiding Comedogenic Ingredients
Avoiding skincare and cosmetic products that contain pore-clogging ingredients, such as mineral oil or lanolin, can also help prevent blackhead formation. Be mindful of product labels and opt for those that are oil-free and non-comedogenic.
Chemical Exfoliation
Chemical exfoliation, using ingredients such as salicylic acid or glycolic acid, can help remove dead skin cells and unclog the pores. Incorporating chemical exfoliants into your skincare routine can assist in minimizing blackheads.
Topical Retinoids
Topical retinoids, derived from vitamin A, can be effective in treating blackheads. They work by increasing cell turnover and preventing the buildup of dead skin cells within the hair follicles and pores.
Extraction by Professionals
In cases where blackheads are persistent or widespread, professional extraction by a dermatologist or esthetician may be necessary. They can safely remove blackheads using specialized tools and techniques, minimizing the risk of scarring or infection.
Professional Dermatological Procedures
In severe cases, dermatological procedures such as chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser treatments may be recommended. These procedures can effectively treat blackheads and improve overall skin texture.
Home Remedies for Blackhead Removal
Steaming and Facial Masks
Steaming the face can help open up the pores and facilitate the removal of blackheads. Applying facial masks containing ingredients like clay or charcoal can further draw out impurities and reduce the appearance of blackheads.
Baking Soda
A paste made from baking soda and water can be used as a gentle exfoliant to remove dead skin cells and unclog the pores. However, individuals with sensitive skin should use caution when using baking soda, as it can be drying and irritating.
Honey
Honey has natural antibacterial properties and can help soothe the skin. Applying a thin layer of raw honey on the affected areas and leaving it for 10-15 minutes before rinsing off can assist in reducing blackheads.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil possesses antibacterial properties and can help reduce inflammation. Diluting tea tree oil with a carrier oil and applying it to the affected areas can potentially aid in getting rid of blackheads.
Clay Masks
Clay masks, particularly those containing ingredients like kaolin or bentonite clay, can absorb excess oil and impurities, making them effective in reducing the appearance of blackheads.
Charcoal
Charcoal-based skincare products, such as cleansers or masks, can help draw out impurities, including blackheads. The activated charcoal acts like a magnet, absorbing excess oil and dirt from the skin.
Cinnamon and Honey
A mixture of cinnamon powder and honey can be used as a natural face mask to help reduce blackheads. Cinnamon has antimicrobial properties, while honey moisturizes and soothes the skin.
Lemon Juice
The acidic nature of lemon juice can help exfoliate the skin and remove dead skin cells. Applying a lemon juice-soaked cotton ball to the affected areas can potentially aid in reducing the appearance of blackheads. However, lemon juice can be drying, so it should be used with caution.
Egg Whites
Applying a thin layer of egg white to the affected areas and allowing it to dry before rinsing off can help tighten the pores and minimize the appearance of blackheads. Egg whites can help remove excess oil and impurities from the skin.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Diluted apple cider vinegar can be used as a toner to help balance the skin’s pH and reduce the risk of blackhead formation. It has natural antibacterial properties and can also help remove excess oil.
Precautions and Best Practices
Avoid Over-Cleansing
While proper cleansing is essential for preventing blackheads, over-cleansing can strip the skin of its natural oils, leading to increased sebum production. It is important to find a balance and avoid excessive cleansing.
Gentle Extraction Techniques
If performing extractions at home, it is crucial to use gentle techniques to avoid damaging the skin or causing scarring. Applying gentle pressure using clean and sterile tools can help minimize the risk of injury and infection.
Avoid Harsh Scrubs and Tools
Avoid using harsh scrubs or tools that can irritate the skin and cause inflammation. Opt for exfoliating products or techniques that are gentle and suitable for your skin type.
Keeping the Skin Moisturized
Moisturizing the skin is essential, even for individuals with oily or combination skin types. Using a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer can help maintain the skin’s moisture balance and prevent excessive sebum production.
Protecting the Skin from Sun Damage
Excessive sun exposure can increase sebum production and contribute to blackhead formation. Applying a broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher can protect the skin from harmful UV rays and minimize the risk of blackhead development.
Avoid Picking or Squeezing Blackheads
Picking or squeezing blackheads can lead to inflammation, infection, and scarring. It is best to avoid touching or manipulating blackheads and instead seek professional assistance for safe and effective extraction.
When to Seek Professional Help
Persistent or Severe Blackheads
If blackheads persist despite home remedies and proper skincare practices, it may be beneficial to seek professional help. A dermatologist or esthetician can assess your skin and provide personalized treatment options.
Excessive Inflammation or Infection
If blackheads become inflamed or infected, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide appropriate treatment and minimize the risk of complications.
Severe Scarring
If blackheads result in significant scarring or hyperpigmentation, professional intervention may be necessary. Dermatological procedures, such as laser treatments or chemical peels, can help minimize the appearance of scars.
Worsening of the Condition
If the blackheads worsen over time or spread to new areas, it is important to consult a healthcare professional. They can assess the underlying causes and recommend appropriate treatment options.
Lack of Improvement with Home Remedies
If home remedies do not show significant improvement or fail to prevent blackhead formation, seeking professional help can provide more effective solutions tailored to your specific needs.
In conclusion, understanding blackheads involves recognizing their formation, the role of sebum, hair follicles, and pores, as well as factors contributing to their development. Differentiating blackheads from other skin blemishes and dispelling common misconceptions is crucial. Prevention and treatment involve adopting proper skincare practices, using non-comedogenic products, and seeking professional help when necessary. While home remedies can provide temporary relief, professional intervention may be required for persistent or severe blackheads. Remember to prioritize gentle extraction techniques, avoid harsh scrubs, and protect the skin from sun damage. With the right knowledge and care, you can effectively manage and reduce the appearance of blackheads.